1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| #include <sys/inotify.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void /* 这一坨函数只是打印出变化事件 */
displayInotifyEvent(struct inotify_event *i)
{
printf(" wd =%2d; ", i->wd);
if (i->cookie > 0)
printf("cookie =%4d; ", i->cookie);
printf("mask = ");
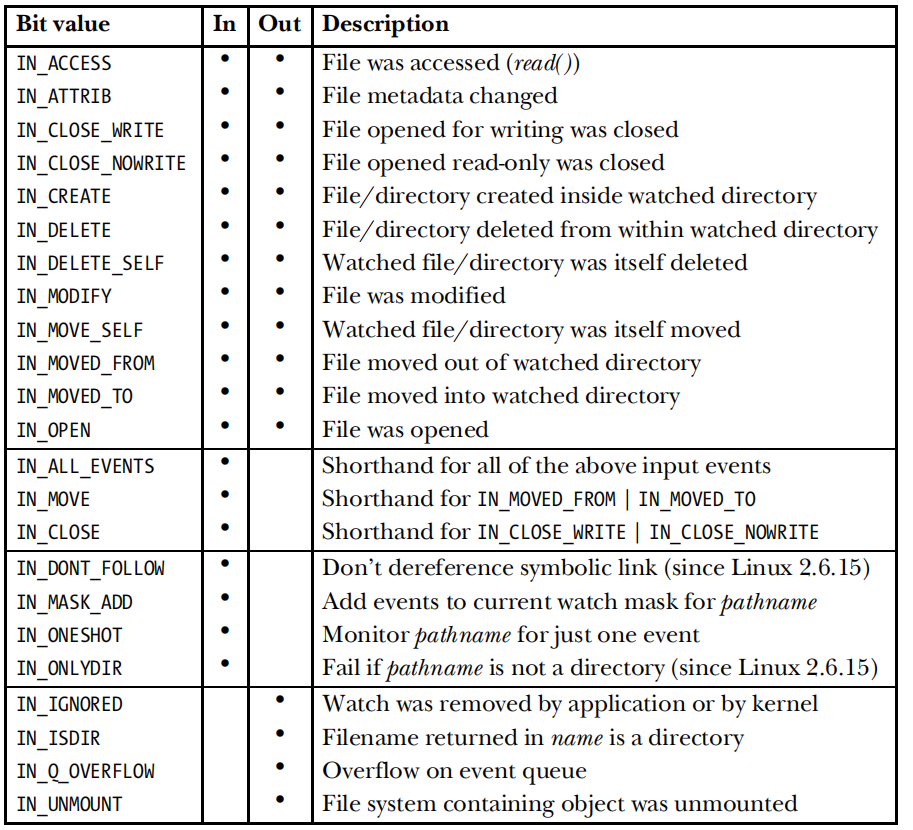
if (i->mask & IN_ACCESS) printf("IN_ACCESS ");
if (i->mask & IN_ATTRIB) printf("IN_ATTRIB ");
if (i->mask & IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE) printf("IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE ");
if (i->mask & IN_CLOSE_WRITE) printf("IN_CLOSE_WRITE ");
if (i->mask & IN_CREATE) printf("IN_CREATE ");
if (i->mask & IN_DELETE) printf("IN_DELETE ");
if (i->mask & IN_DELETE_SELF) printf("IN_DELETE_SELF ");
if (i->mask & IN_IGNORED) printf("IN_IGNORED ");
if (i->mask & IN_ISDIR) printf("IN_ISDIR ");
if (i->mask & IN_MODIFY) printf("IN_MODIFY ");
if (i->mask & IN_MOVE_SELF) printf("IN_MOVE_SELF ");
if (i->mask & IN_MOVED_FROM) printf("IN_MOVED_FROM ");
if (i->mask & IN_MOVED_TO) printf("IN_MOVED_TO ");
if (i->mask & IN_OPEN) printf("IN_OPEN ");
if (i->mask & IN_Q_OVERFLOW) printf("IN_Q_OVERFLOW ");
if (i->mask & IN_UNMOUNT) printf("IN_UNMOUNT ");
printf("\n");
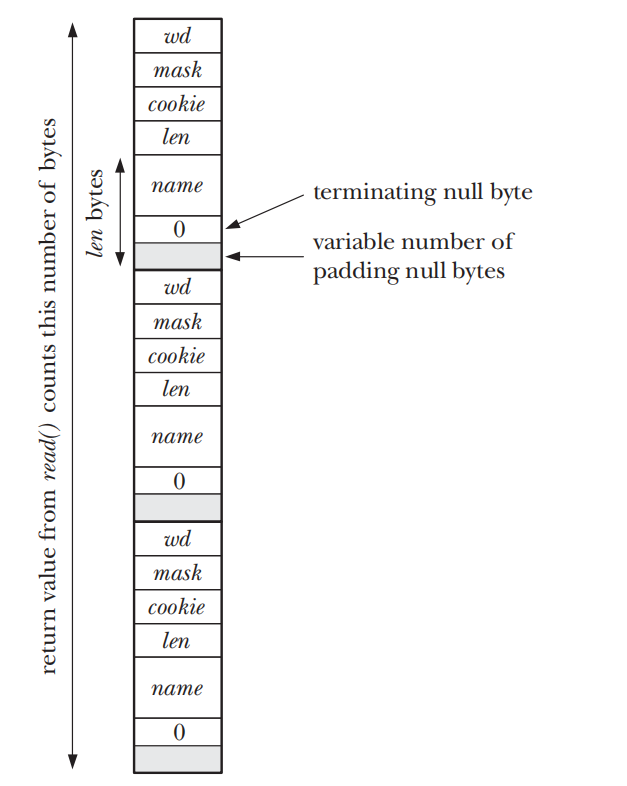
if (i->len > 0)
printf(" name = %s\n", i->name);
}
#define BUF_LEN (10 * (sizeof(struct inotify_event) + NAME_MAX + 1))
/*下面是使用inotify的三个步骤*/
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int inotifyFd, wd, j;
char buf[BUF_LEN];
ssize_t numRead;
char *p;
struct inotify_event *event;
if (argc < 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s pathname... \n", argv[0]);
/*
step 1: 调用inotify_init()创建一个inotify实例
*/
inotifyFd = inotify_init(); /* Create inotify instance */
if (inotifyFd == -1)
errExit("inotify_init");
for (j = 1; j < argc; j++) {
/*
step 2 : int inotify_add_watch(int fd, const char *pathname, uint32_t mask);
添加想要监控的目录路径,mask可以指定监控哪些事件,这里监控所有事件
*/
wd = inotify_add_watch(inotifyFd, argv[j], IN_ALL_EVENTS);
if (wd == -1)
errExit("inotify_add_watch");
printf("Watching %s using wd %d\n", argv[j], wd);
}
for (;;) { /* Read events forever */
/*
step 3 : 读取事件,若没有事件会阻塞
*/
numRead = read(inotifyFd, buf, BUF_LEN);
if (numRead == 0)
fatal("read() from inotify fd returned 0!");
if (numRead == -1)
errExit("read");
printf("Read %ld bytes from inotify fd\n", (long) numRead);
/* Process all of the events in buffer returned by read() */
for (p = buf; p < buf + numRead; ) {
event = (struct inotify_event *) p;
displayInotifyEvent(event);
p += sizeof(struct inotify_event) + event->len;
}
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
|